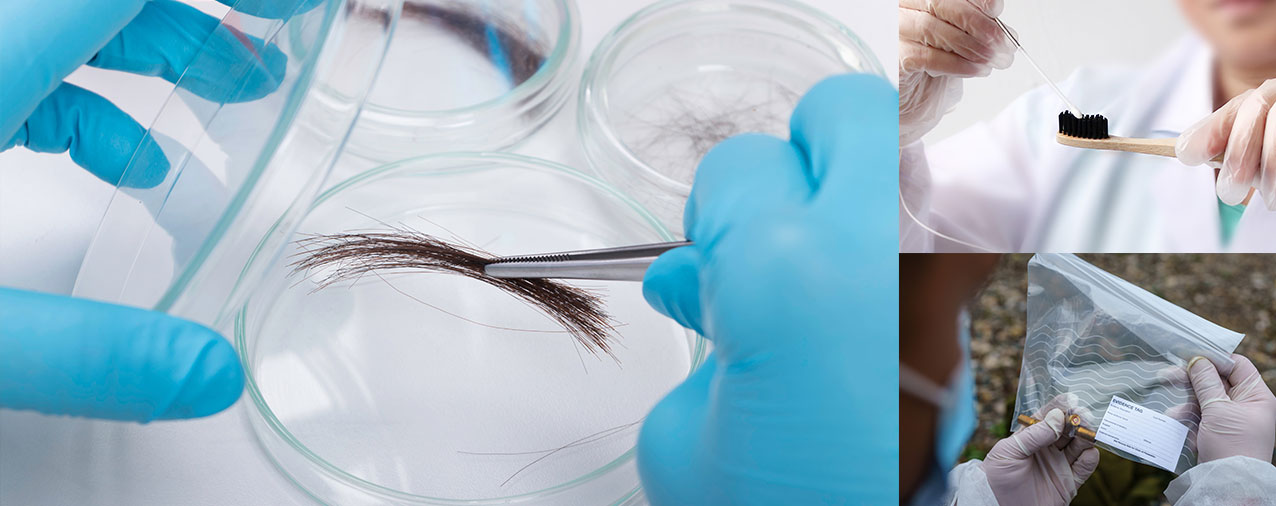
We specialize in processing degraded DNA samples, with over 25 years of experience in forensic identification casework.
Receive your secure and confidential results through your online portal. View your results as soon as they are ready.
All samples are processed by our AABB, ISO17025 & CLIA-certified lab, and never outsourced.
Obtain a viable DNA profile from a forensic sample for identification and kinship comparison purposes.*
Forensic samples are non-conventional samples, such as soiled sheets, blood, tissue, bone, razor blades, toothbrushes etc. and require specialized processing in order to obtain a viable DNA profile.
No two individuals who ever lived are the same – we are all unique. With the exception of identical twins, no two individuals have the same autosomal DNA profile. That’s why autosomal DNA testing is also known as “DNA Profiling” or “DNA Fingerprinting”.
Once a DNA Profile has been obtained, it can be used in a multitude of tests, such as:
| Test Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Matching & Identification | To match the DNA found on a licked envelope, hair sample, or other forensic sample to an individual, whether living or deceased. |
| Paternity testing | To seek the biological father of a child, or to seek the biological child of a father. |
| Maternity testing | To seek the biological mother of a child, or to seek the biological child of a mother. |
| Sibling testing | To seek the full or half biological sibling(s) of an individual. |
| Grandparentage testing | To seek the biological grandmother or grandfather of a child, or to seek the biological grandchild of a grandparent. |
| Aunt/Uncle testing | To seek the aunt or uncle of an individual on both the paternal and maternal lineage. |
*Please note: Due to the variability of forensic sample types, we cannot guarantee viable DNA will be extracted from the sample. We will try our best to obtain a viable DNA sample, however, a non-refundable $350 fee will be applied regardless of whether the sample works or not. Please note that any further testing beyond the standard autosomal DNA profiling product will incur additional costs. These additional tests are not included in the standard cost of the DNA profile. If you have questions please contact us.
Examples of Forensic Samples
Forensic samples are any samples that are not standard mouth swabs. These samples can be used for our DNA tests such as DNA paternity, forensic identification, ancestry and health tests. If you are considering sending a forensic sample, please contact us in advance to discuss your specific case. Examples include:
 Hair Hair |  Toothbrush Toothbrush |  Razor Razor |
 Envelope Envelope |  Tooth Tooth |  Cigarette Cigarette |
 Drinking cup Drinking cup |  Fingernail Fingernail |  Blood stain Blood stain |
 Ear swab Ear swab |  Chewing gum Chewing gum |  Drinking straw Drinking straw |
Please note that any further testing beyond the standard autosomal DNA profiling product will incur additional costs. These additional tests are not included in the standard cost of the DNA profile. If you have questions please contact us.
Introduction to Autosomal DNA
What is it?
Autosomal DNA is the DNA which makes up autosomal chromosomes and are found in the nucleus of the cell. Most cells in our body (somatic cells) contain 23 pairs of chromosomes consisting of 22 pairs of Autosomal chromosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes (the X and Y chromosomes). One copy is of each pair inherited from our biological mother, and the other copy is from our biological father.
We are all unique
No two individuals who ever lived are the same – we are all unique. With the exception of identical twins, no two individuals have the same autosomal DNA profile. That’s why autosomal DNA testing is also known as “DNA Profiling” or “DNA Fingerprinting”.
What is Autosomal DNA Profiling?
Autosomal DNA Profiling (DNA Fingerprinting) usually refers to the testing of STR (short tandem repeat) markers found in Autosomal DNA. STRs are short fragments of DNA, usually 2 to 6 base pairs in length which are repeated over and over again in a defined location of the autosomal DNA. The length of the repeat can vary from person to person, and is inherited within the Autosomal chromosome.
Examining Autosomal STRs
During DNA fingerprinting, a panel of known STR locations (locus, plural loci) are tested to examine the number of repeat “alleles” at each locus. Since each individual has two copies of each autosomal chromosome, each locus will show two possible “alleles”.
An example is locus D5S818 which is found on chromosome #5. D5S818 is known to have repeats ranging from 7 to 17. After testing an individual, the results will show two values, ie. 9, 11. That means the individual inherited a 9 from one parent and an 11 from the other parent.
When a panel of different Autosomal STR markers are examined, the results are known as a “DNA Profile” or “DNA Fingerprint”.
Obtain a viable DNA profile from a forensic sample for identification and kinship comparison purposes.*
Forensic samples are non-conventional samples, such as soiled sheets, blood, tissue, bone, razor blades, toothbrushes etc. and require specialized processing in order to obtain a viable DNA profile.
No two individuals who ever lived are the same – we are all unique. With the exception of identical twins, no two individuals have the same autosomal DNA profile. That’s why autosomal DNA testing is also known as “DNA Profiling” or “DNA Fingerprinting”.
Once a DNA Profile has been obtained, it can be used in a multitude of tests, such as:
| Test Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Matching & Identification | To match the DNA found on a licked envelope, hair sample, or other forensic sample to an individual, whether living or deceased. |
| Paternity testing | To seek the biological father of a child, or to seek the biological child of a father. |
| Maternity testing | To seek the biological mother of a child, or to seek the biological child of a mother. |
| Sibling testing | To seek the full or half biological sibling(s) of an individual. |
| Grandparentage testing | To seek the biological grandmother or grandfather of a child, or to seek the biological grandchild of a grandparent. |
| Aunt/Uncle testing | To seek the aunt or uncle of an individual on both the paternal and maternal lineage. |
*Please note: Due to the variability of forensic sample types, we cannot guarantee viable DNA will be extracted from the sample. We will try our best to obtain a viable DNA sample, however, a non-refundable $350 fee will be applied regardless of whether the sample works or not. Please note that any further testing beyond the standard autosomal DNA profiling product will incur additional costs. These additional tests are not included in the standard cost of the DNA profile. If you have questions please contact us.
Examples of Forensic Samples
Forensic samples are any samples that are not standard mouth swabs. These samples can be used for our DNA tests such as DNA paternity, forensic identification, ancestry and health tests. If you are considering sending a forensic sample, please contact us in advance to discuss your specific case. Examples include:
 Hair Hair |  Toothbrush Toothbrush |  Razor Razor |
 Envelope Envelope |  Tooth Tooth |  Cigarette Cigarette |
 Drinking cup Drinking cup |  Fingernail Fingernail |  Blood stain Blood stain |
 Ear swab Ear swab |  Chewing gum Chewing gum |  Drinking straw Drinking straw |
Please note that any further testing beyond the standard autosomal DNA profiling product will incur additional costs. These additional tests are not included in the standard cost of the DNA profile. If you have questions please contact us.
Introduction to Autosomal DNA
What is it?
Autosomal DNA is the DNA which makes up autosomal chromosomes and are found in the nucleus of the cell. Most cells in our body (somatic cells) contain 23 pairs of chromosomes consisting of 22 pairs of Autosomal chromosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes (the X and Y chromosomes). One copy is of each pair inherited from our biological mother, and the other copy is from our biological father.
We are all unique
No two individuals who ever lived are the same – we are all unique. With the exception of identical twins, no two individuals have the same autosomal DNA profile. That’s why autosomal DNA testing is also known as “DNA Profiling” or “DNA Fingerprinting”.
What is Autosomal DNA Profiling?
Autosomal DNA Profiling (DNA Fingerprinting) usually refers to the testing of STR (short tandem repeat) markers found in Autosomal DNA. STRs are short fragments of DNA, usually 2 to 6 base pairs in length which are repeated over and over again in a defined location of the autosomal DNA. The length of the repeat can vary from person to person, and is inherited within the Autosomal chromosome.
Examining Autosomal STRs
During DNA fingerprinting, a panel of known STR locations (locus, plural loci) are tested to examine the number of repeat “alleles” at each locus. Since each individual has two copies of each autosomal chromosome, each locus will show two possible “alleles”.
An example is locus D5S818 which is found on chromosome #5. D5S818 is known to have repeats ranging from 7 to 17. After testing an individual, the results will show two values, ie. 9, 11. That means the individual inherited a 9 from one parent and an 11 from the other parent.
When a panel of different Autosomal STR markers are examined, the results are known as a “DNA Profile” or “DNA Fingerprint”.
Features
Submit various forensic samples
Submit a variety of forensic samples such as toothbrushes, razors or plucked hair for analysis.
Accredited laboratory
All tests are performed in our AABB, ISO 17025 & CLIA accredited laboratory.

Secure online results
Get 24/7 access to your results and real-time status updates from your secure online account.

Private & confidential
Your data belongs to you. We do not share your data with any third party without your permission.
How it works
Collect your sample
Collect a forensic sample – this could be a toothbrush, razor, tissue sample, blood stain, etc. Contact us if you are unsure what to send.
Send sample to the lab
Send your forensic sample to our laboratory. For specialized shipping, please contact us prior to shipping.
Obtain your DNA Profile
DNA will be extracted from the forensic sample, and a profile will be generated. It is now ready for use in kinship analyses and other DNA tests.
FAQ
Here are the answers to the most frequently asked questions about this test.
This test allows you to submit a forensic sample (not a swab) in order to obtain a DNA Profile. No two individuals (with the exception of identical twins) will have the same DNA Profile. Once a DNA Profile has been obtained, you are able to use it in many applications.
For example, you will be able to use it to identify a match, or to use it in a relationship test.
When you receive results, the report will show a table with two columns. One column is titled “DNA Locus”, and the second column is titled “Allele”. If a successful DNA Profile is obtained, there will be values in the “Allele” column at each Locus. No two individuals will have same DNA profile (unless they are identical twins), so the DNA Profile will be specific to one individual. This information can now be used for statistical analysis or kept in your records.
Please note that this DNA Profile cannot be used for applications such as for ancestry testing or health testing. Viable DNA is required for these types of applications.
Please note that any further testing beyond te standard autosomal DNA profiling product will incur additional costs. These additional tests are not included in the standard cost of the DNA profile. If you have questions please contact us.
We test for 24 STR markers, but please be aware that depending on the quality of the sample submitted, we cannot guarantee all markers will have data. Some of the most basic tests can be run using only 10 markers.
Unlike swabs, forensic sample types are unconventional and can vary in type, age and condition – and processing time can vary on a case-by-case basis. Generally, the turnaround time is 10-14 weeks. This is only an estimate and is not guaranteed.
Unfortunately not – the cremation process destroys biological material, including DNA. However, if an individual is recently deceased we may be able to obtain a DNA Profile from a tissue, blood or hair sample. Contact us to discuss your specific situation.
We recommend you purchase this DNA Forensic Identification test in order to obtain the DNA Profile of one individual, as well as the test type (i.e. paternity, sibling, grandparent test) you wish to perform if a viable DNA profile is obtained. Alternatively, please contact us and we can assist with placing the order for any additional testing as an add-on to your existing DNA Forensic Identification product.
Any additional tests are not included in the standard cost of the DNA profile. If you have questions please contact us.